Theme: Frontiers in Stem Cell and Bio-Banking
Stem Cell Biology 2019
About Conference
Hear, explore and learn the latest research. Present before distinguished global audience. Collaborate, build partnerships and experience Japan. Join the global academic community.
Conference Series invites all the participants across the globe to attend the "13th World Congress on Stem Cell and Bio-Banking" November 11-12, 2019 Tokyo, Japan. Stem Cell Biology 2019 includes prompt keynote presentations, Oral talks, Poster presentations, Young Research Forums(YRF) and Exhibitions.
Stem Cell Biology 2019 aims in proclaim knowledge and share new ideas amongst the professionals, industrialists and students from research area of Stem Cell and Biobanking to share their research experiences and indulge in interactive discussions at the event. This scientific gathering guarantees that offering the thoughts and ideas will enable and secure you the theme “Frontiers In Stem Cell and Bio-Banking”. Stem Cell and Biobanking is the latest trending research in many fields especially in Organ cancer: breast, oral, head and neck Cancer Myeloid, lymphoid leukaemia’s, cancer treatments etc. The current era fully rolled out with many new advanced treatment technologies. In such case more Stem Cells research institutes were newly introduced within market which obviously shows the market growth of Stem Cells and Biobanking. While analyzing the revenue growth of Stem Cells and Biobanking functions, it highly developed from $150 billion USD to $250 billion USD since from 2010-2015. And the annual growth percentage increases from 20-55 percentages.
Importance and Scope
Recently, there has been an increasing demand for quality and trained manpower in this evolving branch of biomedicine. As a result of this, stem cells research is emerging as a rage among the many career options available to people in associated fields. The current investment in stem cell research in India is more than 1000 crores. Most of the investment in stem cell research in India is in the government sector. So, there are a lot of research opportunities on a national front in India.
Why to attend?
With members from around the world focused on learning about Stem Cells and Biobanking, this is your single best opportunity to reach the largest assemblage of participants from the Stem cells research community. Conduct demonstrations, distribute information, acquire knowledge about current and trending Stem cells and Biobanking technologies, make a splash with a new research, and receive name recognition at this 2-day event. World-renowned speakers, the most recent techniques, tactics, and the newest updates in fields are hallmarks of this conference.
Target Audience
- Stem cell researchers and academicians
- Doctorates in Bio- Sciences
- Regenerative medicine Lab Directors/Associates
- Professors of Life sciences
- Biobanking Researchers
- Biobanking Faculty
- Medical Colleges
- Biobanking Associations and Societies
- Business Entrepreneurs
- Training Institutes
- Cryo storage Companies
- Data Management Companies
- Global Biobanking Companies
- Biobanking investors
Conference Highlights
- Stem Cell Therapy
- Genetics and Stem Cell Biology
- Cancer Stem Cells
- Tissue Engineering
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Stem Cell Niche
- Regenerative Medicine
- Adult Stem Cells
- Embryonic Stem Cells
- Stem cell Apoptosis and Signal Transduction
- Computational Biology in Stem Cells
- Epigenetics
- Bio-Banking
- Stem Cell Biomarkers
- Bio-Bank Ethics
- Stem Cell in Drug Development
- Cell and Gene Therapy
- Stem Cell Nanotechnology


It gives me great pleasure to welcome you all to Tokyo, for the World Congress on Stem Cell Biology 2019.
The World Congress on Stem Cell Biology and Biobanking brings together world leading experts to discuss recent findings and progress that is driving the development of stem cell treatments and biobanking.
I encourage my colleagues all to use this event as an opportunity to share ideas and strengthen international relationships in stem cell research and biobanking.
For all world researchers, closer ties mean more opportunities to partner with the best in the world and collaborate on medical breakthroughs that will change lives.
As you take part in this important event, I hope you have the chance to enjoy of Tokyo.

Best regards
Dr. Gramatiuk Svetlana
President Ukraine Association of Biobank
Theme: “Frontiers In Stem Cell Biology and Bio-Banking ’’
World conference on Stem Cell Biology 2019 aims in providing premier interdisciplinary platform for researchers, practitioners and educators to present and discuss the most recent innovations, trends, and concerns as well as practical challenges encountered and solutions adopted in the fields of Stem Cell and Biobanking.
Track 1. Stem Cell Therapy
Stem Cell Therapy (SCT) is the treatment of various disorders, non-serious to life threatening, by using stem cells. These stem cells can be procured from a lot of different sources and used to potentially treat more than 80 disorders, including neuromuscular and degenerative disorders. Stem cells from a donor either from cord blood or bone marrow are known to reconstitute the defective bone marrow and permanently overcome the disorder.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan), .
Track 2. Genetics and Stem Cell Biology
Stem Cell Genomics analyzes the genomes of stem cells. The study of stem cell genomics has wide reaching implications in the study of stem cell biology and possible therapeutic usages of stem cells. Application of research in this field could lead to drug discovery and information on diseases by the molecular characterization of the pluripotent stem cell through DNA and transcriptome sequencing and looking at the epigenetic changes of stem cells and subsequent products.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan), .
Track 3. Cancer Stem Cells(CSC)
Cancer Stem Cells are cancer cells (tumor cells) that possess characteristics associated with normal stem cells, specifically the ability to give rise to all cell types found in a particular cancer sample. CSCs are therefore tumorigenic (tumor-forming), perhaps in contrast to other non-tumorigenic cancer cells. CSCs may generate tumors through the stem cell processes of self-renewal and differentiation into multiple cell types. Such cells are hypothesized to persist in tumors as a distinct population and cause relapse and metastasis by giving rise to new tumors.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan), .
Track 4. Tissue Engineering
Tissue Engineering is the use of a combination of cells, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to improve or replace biological tissues. Tissue engineering involves the use of a scaffold for the formation of new viable tissue for a medical purpose. The goal of tissue engineering is to assemble functional constructs that restore, maintain, or improve damaged tissues or whole organs.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan), .
Track 5. Stem Cells
Stem Cells are characterized by the ability to self-renew, or divide without senescing, and to differentiate into specialized somatic cells. Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into specific cell types. The two defining characteristics of a stem cell are perpetual self-renewal and the ability to differentiate into a specialized adult cell type. There are two major classes of stem cells: pluripotent that can become any cell in the adult body, and multipotent that are restricted to becoming a more limited population of cells. Multiple types of stem cells have been identified, including embryonic and adult stem cells.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan), .
Track 6. Stem Cell Transplantation
Stem Cell Transplantation, sometimes referred to as bone marrow transplant, is a procedure that replaces unhealthy blood-forming cells with healthy cells. Stem cell transplantation allows doctors to give large doses of chemotherapy or radiation therapy to increase the chance of eliminating blood cancer in the bone marrow and then restoring normal blood cell production.
The basis for stem cell transplantation is that blood cells (red cells, white cells and platelets) and immune cells (lymphocytes) arise from the stem cells, which are present in marrow, peripheral blood and cord blood. Intense chemotherapy or radiation therapy kills the patient's stem cells.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan), .
Track 7. Stem Cell Niche
Stem Cell Niche is the in vivo microenvironment where stem cells both reside and receive stimuli that determine their fate. Therefore, the niche should not be considered simply a physical location for stem cells, rather as the place where extrinsic signals interact and integrate to influence stem sell behavior. These stimuli include cell-to-cell and cell-matrix interactions and signals (molecules) that activate and/or repress genes and transcription programs.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan),
Track 8. Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative Medicine is a broad field that includes tissue engineering but also incorporates research on self-healing where the body uses its own systems, sometimes with help foreign biological material to recreate cells and rebuild tissues and organs. The terms “tissue engineering” and “regenerative medicine” have become largely interchangeable, as the field hopes to focus on cures instead of treatments for complex, often chronic, diseases. This field continues to evolve. In addition to medical applications, non-therapeutic applications include using tissues as biosensors to detect biological or chemical threat agents, and tissue chips that can be used to test the toxicity of an experimental medication. Regenerative medicine includes the generation and use of therapeutic stem cells, tissue engineering and the production of artificial organs.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan),
Track 9. Adult Stem Cells
Adult Stem Cells, like all stem cells, share at least two characteristics. First, they can make identical copies of themselves for long periods of time; this ability to proliferate is referred to as long-term self-renewal. Second, they can give rise to mature cell types that have characteristic morphologies (shapes) and specialized functions. Typically, stem cells generate an intermediate cell type or types before they achieve their fully differentiated state. The intermediate cell is called a precursor or progenitor cell. Progenitor or precursor cells in fetal or adult tissues are partly differentiated cells that divide and give rise to differentiated cells.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan),
Track 10. Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryonic Stem Cells are obtained from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst. They can give rise to every cell type in the fully formed body, but not the placenta and umbilical cord. These are incredibly valuable because they provide a renewable resource for studying normal development and disease, and for testing drugs and other therapies. Human embryonic stem cells have been derived primarily from blastocysts.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan),
Track 11. Stem Cell Apoptosis and Signal Transduction
Self renewal and proliferation of stem cell populations is controlled, in part, by induction of apoptosis. The number of stem cells is therefore a balance between those lost to differentiation / apoptosis and those gained through proliferation. Apoptosis of stem cells is believed to be a dynamic process which changes in response to environmental conditions. For example, the release of stem cell factor inhibits apoptosis following spinal cord injury, presumably in an attempt to promote tissue repair. Dysregulation of apoptosis in stem cells is believed to underlie some cancer pathologies, where apoptotic resistance results in uncontrolled growth (i.e. glioblastoma).
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan),
Track 12. Computational Biology in Stem Cells
Computational Biology, a branch of biology involving the application of computer science to the understanding and modeling of the structures and processes of biology, that referred to as bioinformatics. It entails the use of computational methods for the representation and apply advanced analysis techniques that make it possible to dissect complex collections of data from a wide range of technologies and sources.
The fields of stem cell biology and regenerative medicine research are fundamentally about understanding dynamic cellular processes such as development, reprogramming, repair, differentiation and the loss, acquisition or maintenance of pluripotency.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan),
Track 13. Epigenetics
Epigenetics is the study of potentially heritable changes in gene expression that does not involve changes to the underlying DNA sequence - a change in phenotype without a change in genotype -which in turn affects how cells read the genes. Gene expression can be controlled through action of repressor protein that attach to silencer regions of DNA. Many types of epigenetic processes have been identified-they include methylation, acetylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitylation, and sumolyation. Other epigenetic mechanisms and considerations are likely to surface as work proceeds. Epigenetic processes are natural and essential to many organism functions, but if they occur improperly, there can be major adverse health and behavioral effects. One example of an epigenetic change in eukaryotic biology is the process of cellular differentiation.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan),
Track 14. Bio-Banking
Bio-Banking is a type of biorepository that stores biological samples (usually human) for use in research. The wide array of bio specimens (including blood, saliva, plasma, and pure DNA) maintained in biobanks is delineating as libraries of the human organism. They’re rigorously characterized to see the final and distinctive options of the continual cell line and therefore the absence or presence of contaminants, thus establishing a basic understanding regarding the staple from that the biological product is being derived and maintained. Biobanks have become an important resource in medical research, supporting many types of contemporary research like genomics and personalized medicine.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan),
Track 15. Bio-Bank Ethics
Ethical issues are commonly present in many aspects of Biobanking. The fact that Bio banks deal with human samples, invading an individual autonomy or limiting self-control, provokes a number of ethical issues. Who is actually competent to give informed consent and donate a sample? When individuals donate part of their body to a bio bank, how is that human sample processed? Who is the owner of the sample? Who should decide how it should be used? Who has the right to know individual results of research? These and many more ethical dilemmas exist in the ethical framework of bio banks.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan),
Track 16. Stem Cell in Drug Development
Stem Cell Therapy has opened a new avenue in the area of drug discovery and development. Biopharmaceutical companies have been working in deciphering vital applications of stem cell technologies in the drug development processes so as to reduce the high attrition rate of late stage drug candidates, which has been growing at a fast pace in the past decade.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan),
Track 17. Cell and Gene Therapy
Cell Therapy or cryotherapy is the transfer of cells into a patient with a goal of improving the disease. From beginning blood transfusions were considered to be the first type of cell therapy to be practiced as routine. Later, Bone marrow transplantation has also become a well-established concept which involves treatment of much kind of blood disorders including anemia, leukemia, lymphoma and rare immunodeficiency diseases.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan),
Track 18. Stem Cell Bio-Markers
Bio-Marker is a biological molecule found in blood, other body fluids, or tissues that is a sign of a normal or abnormal process, or of a condition or disease. A bio marker may be used to see how well the body responds to a treatment for a disease or condition. In cancer research and medicine, bio markers are used in three primary ways: Diagnostic, Prognostic, Predictive.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan),
Track 19. Stem Cell Nanotechnology
Human beings suffer from a myriad of disorders caused by biochemical or biophysical alteration of physiological systems leading to organ failure. For a number of these conditions, stem cells and their enormous reparative potential may be the last hope for restoring function to these failing organ or tissue systems. To harness the potential of stem cells for biotherapeutic applications, we need to work at the size scale of molecules and processes that govern stem cells fate.
Related societies and association: Motor Neuron Diseases Association, Taiwan Society for Stem Cell Research, Danish Stem Cell Society, Stem Cell Society Singapore, Norwegian Centre For Stem Cell Research, Helmholtz Association Biobank Germany, Brain Bank for Aging Research (Japan).
13th World Congress on Stem Cell Biology and Biobanking
Stem Cell is a broad-spectrum journal that covers the entire spectrum of stem cell biology. Topics covered include embryonic stem cells, pluripotency, germline stem cells, tissue-specific stem cells, stem cell differentiation, epigenetics, stem cell genomics and systems biology, genome reprogramming, cancer stem cells, stem cell niches, stem-cell-based disease models, nuclear transfer technology, bioengineering, drug discovery, in vivo imaging of stem cells, therapeutic applications, regenerative medicine, clinical and translational insights, stem cell research policies, ethical issues, and technical or resource-based innovations.
Why to attend???
Stem Cell Biology 2019 could be an outstanding event that brings along a novel and International mixture of researchers, doctors, leading universities and stem cell analysis establishments creating the conference an ideal platform to share knowledge, adoptive collaborations across trade and world, and assess rising technologies across the world. World-renowned speakers, the most recent techniques, tactics, and the newest updates in cell science fields are assurances of this conference.
Targeted Participants:
- Researchers & Scientists related to Stem cell & Regenerative Medicine R&D
- Deans and Professors
- Directors, CEOs, Presidents and Vice Presidents
- University Faculty
- Medical Schools/Colleges
- Associations and Societies related to Stem cell & Regenerative Medicine R&D
- Stem cell & Regenerative Medicine Program Organizing Government and Non-Government Organizations
- Business Entrepreneurs
- Drug Manufacturing Companies
- Stem cell & Regenerative Medicine Developers and Investigators
History of stem cells research
Stem cells have an interesting history; in the mid 1800s, it was revealed that cells were basically the building blocks of life and that some cells had the ability to produce other cells. Efforts were made to fertilize mammalian eggs outside of the human body and in the early 1900s, it was discovered that some cells had the capacity to generate blood cells. In 1968, the first bone marrow transplant was achieved successfully to treat two siblings with severe combined immunodeficiency. Other significant events in stem cell research include:
1978: Stem cells were discovered in human cord blood
1981: First in vitro stem cells line developed from mice
1988: Embryonic stem cells lines created from a hamster
1995: First embryonic stem cells line derived from a primate
1997: Cloned lamb from stem cells
1997: Leukemia origin found as haematopoietic stem cells, indicating possible proof of cancer stem cells
Market Growth of Stem Cell & Regenerative Medicine Research:
By the year 2025, the global stem cell market is expected to reach USD of 15.63 Billion with a growth of 9.2% in CAGR according to the new report made by Grand View Research, Inc. The market growth is anticipated to be driven by aiming at broadening the utility scope of associated products in Augmentation Research. The research projects have opened the possibility of implementation of several clinical applications through discovering the new regenerative medicine for incurable diseases.
Scientists are engaged in discovering novel methods to create human stem cells. This is to address the increasing demand for stem cell production for potential investigation in disease management. This factor is certainly expected to accelerate the development of regenerative medicine, thus driving industrial growth.
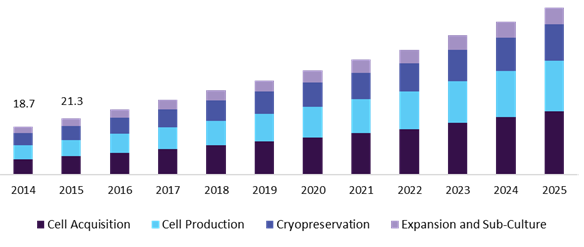
Fig: Market Analysis of Stem Cell Culture
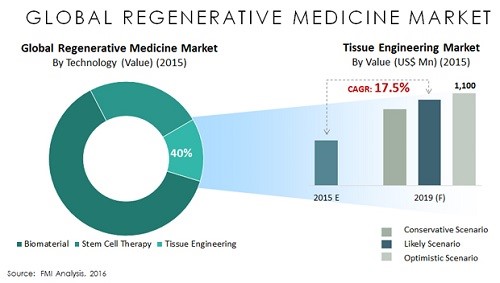
The global Regenerative medicine market is expected to reach USD 38.70 Billion by 2021 from USD 13.41 Billion in 2016 at a CAGR of 23.6% from 2016 to 2021. The major factor driving the growth of this market, are government and private funding to support the development of regenerative medicine, rising prevalence of chronic diseases and genetic disorders, increase in global healthcare expenditure, and rapid growth in the aging population.
The report segments this market based on types, therapy, application, and regions. Based on types, the Regenerative medicine market is segmented into cell-based products and acellular products. In 2016, cell-based products expected to dominate the global Regenerative medicine market. The key drivers include the increasing awareness about stem cell therapy, growing funding for new stem cell lines, and development of advanced genomic methods for cell analysis.
Based on therapy, the Regenerative medicine market is segmented into cell therapy, gene therapy, tissue engineering, and immunotherapy. The cell therapy segment is expected to account for the largest share of this market, increasing funding from several agencies and private organizations for the research and development of cell therapies, growing inclination of the healthcare industry towards stem cell research, and increasing global awareness about the benefits of stem cell therapies.
Fig: Market Analysis of Global Regenerative Medicine
A Unique Opportunity for Advertisers and Sponsors at this International event:
Website URL: http://stemcell.geneticconferences.com/
UAS Major Universities which deals with Stem Cell Research
· University of Washington/Hutchinson Cancer Center
· Oregon Stem Cell Center
· University of California Davis
· University of California San Francisco
· University of California Berkeley
· Stanford University
· Mayo Clinic
Major Stem Cell Organization Worldwide:
· Norwegian Center for Stem Cell Research
· France, I-stem
· Stem Cell & Regenerative Medicine Ctr, Beijing
· Stem Cell Research Centre, Korea
· NSW Stem Cell Network
· Monash University of Stem Cell Labs
· Australian Stem Cell Centre
Companies working for Stem Cell:
|
Company |
Location |
Business Type |
|
Cynata Therapeutics |
Armadale, Australia |
Stem Cell Manufacturing Technology |
|
Mesoblast |
Melbourne, Australia |
Regenerative Medicine |
|
Activartis |
Vienna, Austria |
Dendritic Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy |
|
Aposcience |
Vienna, Austria |
Treatments composed of mixture of cytokines, growth factors and other active components |
|
Cardio3 Biosciences |
Mont-Saint-Guibert, Belgium |
Stem Cell Differentiation |
|
Orthocyte (BioTime) |
Alameda, CA |
Cellular Therapies |
|
Capricor |
Beverly Hills, CA |
Stem Cell Heart Treatments |
|
Life Stem Genetics |
Beverly Hills, CA |
Autologous stem cell therapy |
|
International Stem Cell |
Carlsbad, CA |
Proprietary Stem Cell Induction |
|
Targazyme |
Carlsbad, CA |
Cell Therapy |
|
DaVinci Biosciences |
Costa Mesa, CA |
Cellular Therapies |
|
Invitrx Therapeutics |
Irvine, CA |
Autologous Stem Cell Therapy, Therapeutic & Cosmetic |
References:
http://www.stemcell.com/en/Products/All-Products/EasySep-Mouse-CD25-Regulatory-T-Cell-Positive-Selection- Kit.aspx
- http://www.stemcell.com/en/Products/All-Products/EasySep-Mouse-CD25-Regulatory-T-Cell-Positive-Selection-Kit.aspx
- http://seekingalpha.com/article/1347281-investing-in-the-stem-cell-sector-an-overview
- http://mbbnet.umn.edu/scmap/scresearchmap.html
- http://biopharmguy.com/links/company-by-location-stem-cells.php
- http://www.marketwired.com/press-release/latest-research-shows-stem-cell-product-market-to-reach-6-billion-by-2016-1688406.htm
Conference Highlights
- Stem Cell Therapy
- Genetics and Stem Cell Biology
- Cancer Stem Cells
- Tissue Engineering
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Stem Cell Niche
- Regenerative Medicine
- Adult Stem Cells
- Embryonic Stem Cells
- Stem Cell Apoptosis and Signal Transduction
- Computational Biology in Stem Cells
- Epigenetics
- Bio-Banking
- Bio-Bank Ethics
- Stem Cell in Drug Development
- Cell and Gene Therapy
- Stem Cell Bio-Markers
- Stem Cell Nanotechnology
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | November 11-12, 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Diabetes & Metabolism
- Endocrinology & Diabetes Research
- Journal of Clinical and Molecular Endocrinology
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by